In this article, we are going to discuss how to design an inexpensive 18V transformer less power supply. Linear power supplies typically contain a transformer, which can be a costly component compared to other parts. However, in this article, we will learn how to design an 18V and 40mA power supply without using a transformer. This particular power supply can be useful for low-power projects, such as powering microcontrollers or testing low-power components. If you’re interested, we have previously posted an article on transformerless power supply for microcontrollers. You can check it out by clicking on the following link:
What is a Transformerless Power Supply?
Transformerless power supplies, also known as capacitor-fed power supplies, are commonly used in some electronic applications. These power supplies eliminate the need for a traditional transformer by utilizing a capacitor between the high-voltage and low-voltage sides. The high-voltage side is connected to the main AC power source, while the low-voltage side powers the electronic circuitry. However, it’s important to note that capacitor power supplies can pose certain risks and require careful handling and design considerations for safe operation.
Circuit Diagram of Transformerless Power Supply
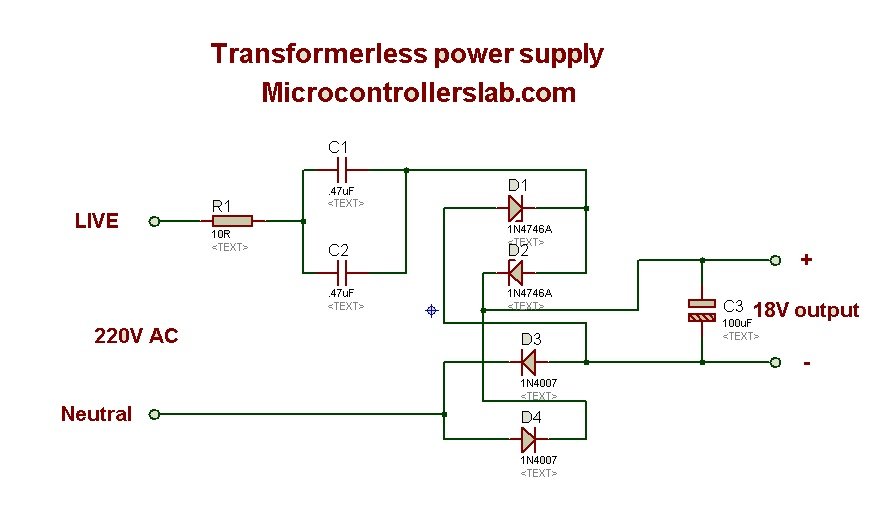
The circuit diagram represents a transformerless power supply, designed to provide an output voltage of 18V and a maximum current of 40mA. Let’s take a closer look at the components and the working of this circuit:
Components
- R1 (10-ohm resistor): This resistor acts as a safety fuse resistor and also helps in limiting the current flow through the circuit.
- C1 and C2 (.47uF capacitors): These capacitors are connected in parallel and function as an oscillator. They produce a pulsating AC voltage at the output of the full bridge rectifier circuit.
- C3 (100uF capacitor): This capacitor is used to filter the pulsating AC voltage produced by the full bridge rectifier and provides a relatively constant DC voltage at the output.
- D1 and D2 (1N4746A zener diodes): These diodes are utilized as voltage regulators. They ensure that the output voltage does not exceed 18 volts by clamping the pulsating DC voltage.
- D3 and D4 (1N4007 rectifier diodes): These diodes are part of the full bridge rectifier circuit. They rectify the incoming AC voltage, converting it into pulsating DC voltage that is then filtered by the capacitors.
Working
- The circuit is connected to the main AC power source. The high voltage side, which is connected to the AC source, goes through the path highlighted by the red arrows in the circuit diagram.
- The incoming AC voltage is rectified by the D3 and D4 diodes in the full bridge rectifier circuit. This converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage.
- The pulsating DC voltage is then filtered by the combination of C1, C2, and C3 capacitors. C3 helps in smoothing out the pulsations and provides a relatively stable DC voltage at the output.
- The output voltage is clamped at a maximum of 18 volts by the D1 and D2 zener diodes, which act as voltage regulators.
- The 10 ohm resistor R1 acts as a safety fuse resistor and limits the current flow through the circuit.
- The resulting DC voltage, approximately 18 volts, is available at the output of the circuit.
It’s important to note that transformerless power supplies, including this circuit, have certain risks associated with them. Careful handling and design considerations are necessary for safe operation.
Applications
Transformerless power supplies have various applications due to their compact size and cost-effectiveness. Some of the applications of an 18V transformerless power supply include:
- Low-Power Electronics: The 18V transformerless power supply is ideal for low-power electronic projects, such as powering microcontrollers, Arduino boards, or other small electronic devices that require a stable and reliable power source.
- Sensor Circuits: Many sensor circuits, such as temperature sensors or light sensors, operate at low voltages and require an efficient and compact power supply. The 18V transformerless power supply can provide the necessary power for such sensor circuits.
- IoT (Internet of Things) Devices: With the increasing popularity of IoT devices, which require small and efficient power supplies, the 18V transformerless power supply can be used to power various IoT devices such as smart sensors, smart home automation systems, or wearable devices.
- Battery Chargers: The 18V transformerless power supply can be utilized as a compact power source for charging batteries of low-power devices, such as mobile phones, portable speakers, or battery-powered tools.
- Educational Projects: The simplicity and cost-effectiveness of transformerless power supplies make them suitable for educational projects and learning purposes. Students and hobbyists can use the 18V transformerless power supply to power their electronic projects and gain hands-on experience.
- Testing Low-Power Components: When testing low-power electronic components or circuits, it is essential to have a stable and low-voltage power supply. The 18V transformerless power supply can provide a reliable power source for testing and evaluating such components.
- DIY Electronics: For DIY enthusiasts, the 18V transformerless power supply can be a useful tool for powering various home automation projects, robot kits, or other DIY electronic gadgets.
It’s important to note that while transformerless power supplies offer advantages in terms of cost and size, they also have certain risks and safety considerations. Careful design, insulation, and adherence to electrical safety practices are essential to ensure safe operation and minimize the risk of electric shock or short circuits.
Recommended reading:
- Smart under and over voltage protection system for home
- Automatic dark detection circuit with Alarm
- Automatic street light control circuit diagram
- Three Phase Sine Wave Generator Circuit
- Automatic globe light control circuit
- DTMF Controlled Home Automation System
- Automatic plant watering system circuit diagram
You did not mention the voltages of the capacitors
The .47 uF, 400V, since they’re connected to 220 V AC.
The 100 uF, 25V at least.
you did not mentioned the voltages of three capacitors and wattege of resistor and diodes