SIM300D is basically designed for the global market. It is a tri-band GSM/GPRS modem that works on frequencies EGSM 900 MHz, DCS 1800 MHz, and PCS 1900MHz. This module provides GPRS multi-slot class 10 potential and supports GPRS coding schemes. It has a lot of applications in PIC microcontroller-based projects. SIM300D GSM module is very popular among engineering students. They use it to make innovative electrical and electronics projects. To make GSM-based projects, you should first know about GSM interfacing with a microcontroller. Sim900D GSM module is also available in the market.
SIM300D Introduction
The SIM300D is a GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) module that is designed for use in various communication applications. It is part of the SIMCOM SIM300 series of GSM modules, which are widely used in embedded systems and IoT (Internet of Things) devices for cellular communication.
Features
Here are some key features and aspects of the SIM300D GSM module:
GSM Communication: The SIM300D module allows devices to communicate over GSM networks, making it suitable for sending and receiving SMS (Short Message Service) messages, making voice calls, and establishing data connections.
Quad-Band Support: It typically supports quad-band GSM frequencies, which means it can operate on GSM networks in multiple regions around the world, including 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz bands.
Serial Communication: The module communicates with the host microcontroller or system using a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) serial interface. This makes it easy to integrate into embedded systems.
AT Commands: Communication with the SIM300D module is typically done by sending AT (Attention) commands over the serial interface. These commands are used to configure the module and instruct it to perform various functions, such as sending SMS messages or making calls.
SIM Card Slot: The module has a SIM card slot where you insert a SIM card from a mobile network operator. This SIM card is used for authentication on the network.
Various Interfaces: It may provide additional interfaces like GPIO (General-Purpose Input/Output) pins, analog interfaces, and more, depending on the specific module variant.
Low-Power Mode: Some SIM300D modules support low-power modes to conserve energy when not actively transmitting or receiving data.
Embedded Applications: The SIM300D and similar GSM modules are commonly used in applications such as remote monitoring, tracking systems, security systems, and any application where remote communication via cellular networks is required.
External Antenna: To ensure good signal reception, the module often requires an external GSM antenna connected to an appropriate antenna port.
Development and Integration: Developers typically write firmware or software to interact with the module and configure it for specific tasks. Integration often involves designing the hardware connections, power supply, and antenna arrangement.
SIM300D GSM module Power Supply
We have given the feeding of energy to a SIM300 of a simple source of VBAT= tension 3.4V… 4.5V. In a sure case that we have, the undulation in a transmission glare can produce because the voltage drops when I use it current emerges to the typical maximums of 2A, so the energy feeding would have to be intelligent in order to supply the sufficient current that is until 2A .
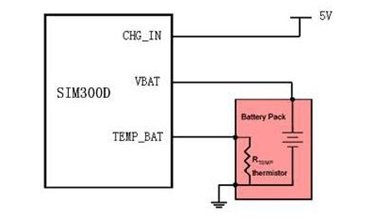
SIM300D GSM module Charging Interface
SIM300D understood a circuit of loading inside the module to control the loading of lithium-ion batteries, which makes it well-suited for applications requiring direct battery charging. A common connection for the charger is indicated in the following figure:
SIM300D GSM module Serial Interface
This GSM module is also capable of providing two asynchronous serial ports, which may be unequal. The GSM functions as a DCE (Data Communication Equipment). Following the conventional DCE-DTE (Data Terminal Equipment) connection, the GSM (DCE) and the client (DTE) are connected through the following signals.
SIM300D GSM Module SIM Interface
The SIM interface is powered by an internal controller in the module that has a nominal voltage of 2.8V. All the pins are reset as outputs, driving low. The circuit diagram for the SIM connection with the SIM300D modem is provided.
SIM300D AT Commands
The SIM300D module, like many GSM modules, communicates with the host controller or device using AT (Attention) commands sent over a serial UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interface. These commands are used to configure the module, control its operation, and send/receive data.
Common AT Commands Examples
Below are some common AT commands for the SIM300D module:
- AT: Test command to check if the module is responsive.
- AT+CPIN=”PIN”: Enter the SIM card’s PIN code for authentication.
- AT+CMGF=1: Set the SMS text mode format for sending and receiving SMS messages.
- AT+CMGS=”PhoneNumber”: Send an SMS message to the specified phone number. After entering this command, the module will expect you to provide the message content and terminate it with Ctrl+Z.
- AT+CMGR=Index: Read an SMS message from the message storage. Replace Index with the index of the message to be read.
- AT+CMGD=Index: Delete an SMS message from the message storage. Replace Index with the index of the message to be deleted.
- ATDPhoneNumber;: Dial a phone number for voice call. Replace PhoneNumber with the desired phone number. Use ATH to hang up the call.
- ATA: Answer an incoming voice call.
- ATH: Hang up an active voice call.
- AT+CREG?: Check the registration status with the GSM network.
- AT+CSQ: Check the signal strength (RSSI) and the bit error rate (BER) of the network.
- AT+COPS=?: List available mobile network operators.
- AT+COPS=0,0,”OperatorName”: Manually select a mobile network operator. Replace “OperatorName” with the desired operator’s name.
- AT+CGATT=1: Attach to the GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) network.
- AT+CIPSTART=”TCP”,”IPAddress”,”Port”: Establish a TCP connection to a remote server. Replace “IPAddress” and “Port” with the server’s details.
- AT+CIPSEND: Initiate data transmission after establishing a TCP connection. After issuing this command, you can send data to the server.
- AT+CIPCLOSE: Close an active TCP connection.
- AT+CGNSPWR=1: Enable GPS (if supported) on the module.
- AT+CGNSINF: Retrieve GPS location information (if supported).
- AT+CGNSPWR=0: Disable GPS.
These are just a few examples of the many AT commands available for controlling the SIM300D module. The exact set of supported commands may vary depending on the firmware version of the module, so it’s important to refer to the module’s datasheet and documentation for the specific command set and usage guidelines for your particular module variant.
Related content:
- SIM900A GSM Module
- Sending Data from GSM module to a Web Server using Arduino
- GSM Based Home Automation project using Arduino
- SIM900A GSM Module Interfacing with Arduino
- Receive SMS GSM Module using pic microcontroller
- How to Answer Phone Call using GSM Module and Computer
- How to Make Call using GSM Module on Mobile Phone
- Send sms using gsm module and pic microcontroller