In the last tutorial, we have seen an introduction to IoT. In this tutorial, we will talk about IoT protocols and their types. If we look closely at the term “Internet of Things”, it has two main words, Things and the Internet. Firstly, for the term “Internet”, the first thing that comes to mind is a network that is used for global communication, thus enabling information sharing across the globe, turning this planet into a global village. On the other hand, the other word “Things” refers to numerous IoT (Internet of Things) devices that are capable of performing actuating, remote sensing and live monitoring of different types of data. Additionally, all these IoT devices have unique identities, so they can be accessed over thousands of devices for the purpose of communication or any other.
A huge number of connected devices making the Internet of Things (IoT) are expanding continuously across the globe. Now, a number of devices around us are capable of processing, collecting, and sending data over servers or other connected devices. These devices are also used in many other ways, such as manufacturing, automotive, medicine, security systems, and much more. Therefore, let’s talk about IoT protocols and types of IoT protocols.
IoT Protocols Introduction
The IoT system can only perform and transfer information when it’s in online mode, which means the devices in IoT must be safely connected to communication networks. The question that arises is how these devices can connect and communicate with each other. The answer lies in PROTOCOLS. Protocols enable these devices to communicate effectively, and new protocols continue to be introduced regularly. In this article, we will discuss the IoT network requirements, and the different types of protocols used in IoT, and provide a brief description of commonly used protocols in the Internet of Things.
Why do we need IoT Protocols?
IoT protocols are essential for enabling seamless and efficient communication between Internet of Things (IoT) devices, applications, and services. They serve as the rules and standards that govern how devices in an IoT ecosystem exchange data and interact with each other. The need for IoT protocols arises due to several reasons:
Interoperability: In IoT, devices come from various manufacturers, and they may use different communication technologies and data formats. IoT protocols ensure that devices from different vendors can communicate and work together seamlessly, fostering interoperability and creating a unified IoT ecosystem.
Efficient Communication: IoT protocols are designed to optimize data transmission and reduce unnecessary overhead, leading to efficient use of resources like power and bandwidth. This efficiency is crucial, especially for IoT devices with limited processing capabilities and battery life.
Security: IoT devices often handle sensitive data and are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. IoT protocols incorporate security mechanisms like encryption, authentication, and data integrity checks to ensure secure communication and protect against unauthorized access.
Scalability: IoT deployments can involve a large number of devices spread across wide areas. IoT protocols are designed to handle scalability, allowing the network to accommodate a growing number of devices without compromising performance.
Low Power Consumption: Many IoT devices are battery-powered or operate in energy-constrained environments. IoT protocols, especially those designed for low-power communication, help extend the battery life of devices and minimize energy consumption.
Real-time Communication: Some IoT applications, such as industrial automation and healthcare monitoring, require real-time data exchange. IoT protocols cater to such scenarios and ensure timely delivery of critical information.
Standardization: IoT protocols are standardized to ensure consistency and compatibility across different implementations. This standardization facilitates the development of a diverse range of IoT devices and applications while ensuring they can work together smoothly.
Data Management: IoT protocols define how data is structured, transmitted, and processed, facilitating efficient data management and analysis. Proper data handling is essential for making informed decisions and deriving meaningful insights from IoT-generated data.
In conclusion, IoT protocols are the backbone of the IoT ecosystem, providing the rules and guidelines necessary for devices to communicate effectively, securely, and reliably. They play a critical role in creating a cohesive and interoperable IoT environment, enabling the realization of the full potential of IoT technologies across various industries and applications.
IoT Networks Requirments
Some mandatory requirements to build an IoT network are listed below:
- Scalable i.e. can connect a large number of devices
- Highly reliable
- Support data transmission in real time with minimized delays
- Protect data flows
- Capable of configuring applications
- Traffic management and monitoring at device level
- It should be cost-effective so that large number of devices can be connected.
IoT Protocol Types
Although, there exist a large number of IoT protocols are used in IoT. but here we will be discussing some widely used protocols in the Internet of Things which are listed below:
- MQTT (message queue telemetry transport)
- DDS (data distribution service)
- AMQP (advance message queuing protocol)
- Bluetooth
- Zigbee
- Wi-Fi
- Cellular
- LoRaWAN
So let’s discuss these protocols in detail.
MQTT Protocol
MQTT is a lightweight protocol specifically designed for sending data from sensors to middleware and applications. It operates on top of TCP/IP, ensuring reliable data delivery. MQTT consists of three main components: Subscriber, Publisher, and Broker. Let’s explore how these components work together in the basic workflow of this protocol, where the publisher generates and transmits information to subscribers through a broker.
Understanding MQTT
MQTT, short for Message Queue Telemetry Transport, is an IoT protocol that excels in lightweight data transfer. Its primary purpose is to enable efficient communication by transmitting data from sensors to middleware and applications.
Reliable Data Delivery
MQTT leverages TCP/IP as its underlying technology, ensuring dependable and secure data delivery. This reliability is essential for real-time and critical IoT applications.
The Three Main Components
MQTT comprises three key components: Subscriber, Publisher, and Broker, each with specific roles.
Subscribers receive data from the publisher through the broker, facilitating seamless data flow.
The Basic Workflow
In MQTT’s basic workflow, the publisher is responsible for generating and transmitting information.
The broker acts as an intermediary, managing the data and delivering it to the relevant subscribers.
You may also like to read projects available on our blog related to MQTT:
- Raspberry Pi Pico W MQTT Client Publish Subscribe Messages
- MicroPython ESP32 MQTT Publish Multiple Sensor Readings to Node-Red
- ESP8266 NodeMCU MQTT Publish Subscribe BME280 Readings with Arduino IDE
- Install Mosquitto MQTT Broker on Windows and Linux
- Install Mosquitto MQTT Broker on Raspberry Pi
LWM2M
Lightweight M2M (LWM2M) is a protocol designed specifically for managing and communicating with IoT devices in a resource-constrained environment. It is a part of the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) Lightweight M2M protocol suite. LWM2M aims to provide a standardized and efficient way to manage devices and their data in IoT deployments.
LWM2M employs a client-server architecture, where IoT devices act as clients and communicate with a management server. The protocol operates over various underlying transport protocols, such as CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) and UDP, which contributes to its lightweight and low-power characteristics. With its small overhead and optimized message format, LWM2M is suitable for devices with limited processing power, memory, and battery life.
One of the key advantages of LWM2M is its extensive range of device management capabilities. It allows for remote device provisioning, firmware updates, monitoring of device status, and reporting of various device parameters. LWM2M also defines a well-organized object and resource model, providing a standardized way to represent device information and functionality. This model simplifies device management and enables interoperability between different IoT platforms and vendors.
Overall, Lightweight M2M is a crucial protocol for the efficient and scalable management of IoT devices in constrained environments. Its lightweight nature, standardized data representation, and robust device management capabilities make it an ideal choice for a wide range of IoT applications, including smart cities, industrial IoT, and healthcare.
DDS (Data Distribution Service)
DDS, which stands for Data Distribution Service, is a powerful protocol widely used in IoT for its scalability, real-time capabilities, and high-performance machine-to-machine communication. This versatile protocol can be implemented in both IoT devices and cloud environments. DDS operates with two primary layers that contribute to its efficient functioning:
DCPS (Data-Centric Publish Subscriber)
The DCPS layer is responsible for delivering information to the subscribers in the DDS ecosystem.
It ensures seamless data distribution, enabling real-time communication among devices and applications.
DLRL (Data Local Reconstruction Layer)
The DLRL layer serves as an interface to support the functions of DCPS.
It plays a vital role in data reconstruction, enabling devices and applications to interact effectively within the DDS environment.
AMQP
AMQP stands for Advanced Message Queuing Protocol. It is a messaging protocol used in the application layer of the OSI model, which is a standard way of organizing how different parts of the internet work together. AMQP’s processing involves three main components, each following specific rules.
Exchange: This component receives messages and places them into queues. It acts as a mediator that ensures messages are delivered to the right destination.
Message Queue: The message queue stores the messages until they are safely processed by client applications. It acts as a buffer, holding messages until they can be handled by the intended recipients.
Binding: The binding defines the relationship between the exchange and the message queue, essentially connecting the two components. It ensures that messages from the exchange are correctly routed to the appropriate message queue for processing.
In summary, AMQP is a sophisticated messaging protocol used to enable efficient and reliable communication between different parts of a system or network. It relies on three main components: the exchange for receiving and directing messages, the message queue for temporary storage, and the binding to establish the link between the exchange and the message queue. These components work together to ensure smooth message delivery and processing in various applications and systems.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) are both wireless communication protocols used in the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable data exchange between devices over short distances. While they share some similarities, they have distinct characteristics and applications.
BLE, also known as Bluetooth Smart, is a variation of Bluetooth designed specifically for low-power and energy-efficient IoT applications. BLE operates in the same 2.4 GHz frequency band as Bluetooth but uses a different modulation scheme, resulting in reduced power consumption. This makes BLE well-suited for IoT devices that run on limited battery power and need to operate for extended periods.
BLE is commonly used in a wide range of IoT devices, including wearable devices, smart sensors, and other IoT-enabled gadgets. It enables intermittent data transmission, allowing devices to remain in a low-power sleep mode for most of the time and only wake up to transmit or receive data when needed. This characteristic greatly extends the battery life of BLE-enabled devices.
In summary, both Bluetooth and BLE are essential IoT protocols for short-range wireless communication. Bluetooth is suitable for applications that require higher data transfer rates and real-time communication, while BLE is ideal for low-power IoT devices that need to conserve energy and operate for extended periods on limited battery power. The choice between Bluetooth and BLE depends on the specific requirements and power constraints of the IoT application at hand.
Zigbee Protocol
Zigbee 3.0 is another important protocol we will explore. It was created by the Zigbee Alliance, and it introduced a universal language called Dotdot for IoT devices. This language enables smart devices to communicate seamlessly and securely across various networks by understanding each other’s commands and data.
Zigbee 3.0 offers several key features:
Low Power: It is designed to be energy-efficient, making it suitable for IoT devices that need to conserve battery life and operate for extended periods.
Low Data Rates: Zigbee 3.0 falls into the category of wireless protocols that offer low data transfer rates. It is ideal for applications where high bandwidth is not a requirement.
Industrial Use: Zigbee 3.0 is commonly used in industrial settings, where reliable and low-power communication between devices is essential for efficient operations.
Based on IEEE 802.15.4 Standard: Zigbee 3.0 follows the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which defines the physical and media access control layers for low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs).
Frequency and Range: Zigbee 3.0 operates at a frequency of about 2.4 GHz, allowing for efficient and widespread communication. Its range typically varies from 10 to 100 meters, depending on the environment and interference.
Data Rate: The data rate of Zigbee 3.0 is around 250 kbps, enabling sufficient data exchange for various IoT applications without overwhelming the devices with data traffic.
In summary, Zigbee 3.0 is a reliable and energy-efficient IoT protocol widely used in industrial settings. Its low-power characteristics, low data rates, and adherence to the IEEE 802.15.4 standard make it a suitable choice for a range of IoT devices and applications where efficient and secure communication is crucial.
LoraWAN
LoRaWAN, which stands for Long Range Wide Area Network, is a wireless communication protocol specifically designed for long-range, low-power IoT applications. It is a part of the LoRa (Long Range) technology ecosystem and is optimized to provide connectivity for IoT devices spread over large geographic areas.
Key features of LoRaWAN as an IoT protocol:
Long Range: LoRaWAN is known for its exceptional long-range capabilities, allowing IoT devices to communicate over several kilometers in open areas. This extended range makes it ideal for applications that require connectivity across vast distances, such as smart agriculture, asset tracking, and smart city deployments.
Low Power: One of the significant advantages of LoRaWAN is its low power consumption. IoT devices using LoRaWAN can operate on batteries for years without needing frequent replacements, making it suitable for remote and hard-to-reach locations where power sources may be limited.
Wide Area Coverage: LoRaWAN’s wide area coverage enables the creation of large-scale IoT networks with minimal infrastructure. Fewer gateways can cover vast regions, reducing the cost of network deployment and maintenance.
Scalability: LoRaWAN is highly scalable, allowing the network to accommodate a massive number of IoT devices. It can support millions of connected devices while maintaining efficient data transfer and minimal interference.
Secure Communication: LoRaWAN incorporates advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure secure communication between IoT devices and the network server, safeguarding data privacy and integrity.
Suitable for Low Data Rate Applications: LoRaWAN is most effective in applications that do not require high data transfer rates. It is ideal for transmitting small amounts of data at regular intervals, making it perfect for sensors, meters, and other low-bandwidth IoT devices.
In summary, LoRaWAN is a robust and cost-effective IoT protocol tailored for long-range, low-power, and scalable communication. Its ability to cover extensive areas and support a vast number of devices with minimal power consumption makes it an excellent choice for diverse IoT applications where long-distance connectivity and efficiency are critical.
Z-wave
Z-Wave is a popular wireless communication protocol designed specifically for home automation and Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It is a proprietary protocol developed by Z-Wave Alliance, a consortium of companies working to standardize and promote the adoption of Z-Wave technology in smart homes.
Key features of Z-Wave as an IoT protocol:
Mesh Networking: Z-Wave operates on a mesh networking topology, where each Z-Wave device (node) acts as a repeater, extending the range and enhancing the reliability of the network. This mesh architecture allows devices to communicate with each other directly or through neighboring nodes, ensuring robust and efficient communication even in larger homes.
Low Power Consumption: Z-Wave is engineered to be power-efficient, making it well-suited for battery-powered devices like smart sensors and door locks. Devices can operate for extended periods on a single battery charge or with minimal power usage.
Interoperability: Z-Wave devices from different manufacturers can seamlessly communicate with each other due to strict certification standards maintained by Z-Wave Alliance. This ensures interoperability and compatibility, allowing users to create a diverse and integrated smart home ecosystem.
Wide Range of Devices: Z-Wave supports a wide range of smart home devices, including lighting controls, thermostats, security sensors, door locks, and more. The extensive selection of Z-Wave devices available in the market enables users to create comprehensive and customizable smart home solutions.
Secure Communication: Z-Wave utilizes AES-128 encryption to ensure secure communication between devices. This encryption helps protect sensitive information and prevents unauthorized access to the network.
Easy Installation: Z-Wave devices are designed for easy installation and setup. Many Z-Wave devices can be added to the network simply by pressing a button or scanning a QR code, making the smart home setup process user-friendly and straightforward.
In summary, Z-Wave is a reliable, low-power, and interoperable IoT protocol tailored for home automation and smart home applications. Its mesh networking architecture, wide range of devices, and secure communication ensure seamless integration and enhanced convenience in creating smart and connected homes. As a result, Z-Wave has gained significant popularity in the smart home industry and continues to be a prominent IoT protocol for home automation.
Thread
Thread is an open, secure, and low-power wireless communication protocol specifically designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It is a reliable mesh networking protocol developed by the Thread Group, an organization consisting of industry leaders collaborating to promote the adoption and interoperability of Thread technology.
Key features of Thread as an IoT protocol:
Mesh Networking: Thread operates on a mesh networking architecture, where each device in the network (node) acts as a router, relaying messages to other devices. This mesh topology ensures robust and efficient communication, even in large-scale IoT deployments.
Low Power Consumption: Thread is optimized for low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated IoT devices. Devices can remain in sleep mode for extended periods, conserving energy and prolonging battery life.
IPv6 Support: Thread natively supports IPv6, enabling direct and seamless integration with the internet. This feature allows Thread devices to communicate with other IPv6-enabled devices and cloud services, expanding the IoT ecosystem’s reach.
Secure Communication: Thread incorporates advanced security mechanisms, including AES encryption and device authentication, to ensure secure communication and protect data privacy in the network.
Interoperability: Thread promotes interoperability between different manufacturers’ devices, adhering to a standardized certification process. This allows users to build multi-vendor IoT systems with confidence in seamless communication.
Easy Setup: Thread is designed to be user-friendly, offering easy setup and configuration. Devices can be added to the network through simple user interactions, such as scanning a QR code or pressing a button, streamlining the IoT device integration process.
Reliable and Scalable: Thread’s mesh networking ensures a reliable connection, even if some nodes experience temporary connectivity issues. Additionally, the protocol is scalable, supporting large IoT networks with thousands of devices.
In summary, Thread is a robust and secure IoT protocol that excels in low-power mesh networking, enabling efficient and reliable communication among IoT devices. Its support for IPv6 and interoperability standards ensures seamless integration with other IoT ecosystems and the internet. With its focus on power efficiency, security, and scalability, Thread is an increasingly popular choice for various IoT applications, including smart homes, industrial automation, and smart cities.
Matter
Matter, formerly known as Project CHIP (Connected Home over IP), is a new and promising IoT protocol designed to enhance smart home interoperability and connectivity. It is developed collaboratively by major technology companies, including Apple, Google, Amazon, and the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA, formerly known as the Zigbee Alliance). Matter aims to create a unified, secure, and reliable standard for smart home devices to communicate seamlessly with each other and integrate into various ecosystems.
Key features of Matter as an IoT protocol:
Interoperability: Matter focuses on promoting interoperability among different smart home devices, regardless of the manufacturer. This means that Matter-compliant devices will work together smoothly, eliminating the need for separate ecosystems or proprietary bridges.
IP-Based Protocol: Matter is built on IP (Internet Protocol), specifically using IPv6, which enables direct communication between devices and the internet. This allows for easy integration with cloud services and enhances remote access and control of smart home devices.
Secure Communication: Security is a core aspect of Matter’s design. It implements the latest encryption standards and secure communication practices, protecting users’ data and privacy. This is crucial for smart home devices that handle sensitive information and perform essential functions like door locks and security cameras.
Wide Range of Devices: Matter is intended to support a broad spectrum of smart home devices, including lights, thermostats, door locks, smart speakers, and more. This inclusivity ensures that a diverse set of devices can seamlessly interact and work together within the smart home ecosystem.
Easy Setup and Control: Matter aims to provide a user-friendly setup process, allowing consumers to effortlessly add new devices to their smart homes. Additionally, it focuses on creating a cohesive and intuitive user experience across various device types and brands.
Open Source and Collaborative: Matter is open-source, allowing developers to contribute to its development and implementation. The collaborative nature of Matter’s development ensures that it reflects the needs and feedback of a wide range of stakeholders in the IoT industry.
In summary, Matter is a promising IoT protocol that strives to create a standardized and interoperable smart home ecosystem. By focusing on IP-based communication, security, and ease of use, Matter aims to simplify the integration and control of smart home devices, making the smart home experience more accessible and enjoyable for consumers. As the adoption of Matter grows and more devices become compatible, it has the potential to revolutionize the smart home industry and set new standards for IoT connectivity and interoperability.
Wi-Fi
In LAN environments, the most used type of connectivity is Wi-Fi. It is the technology that is used in radio wireless networking of devices. Below are some features of this protocol
- Fast data transfer is offered by this protocol
- It can be used to process large amount of data
- It is based on IEEE 802.11 standard
- Frequencies are of about 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands
- Range is approximately 50 m.
- Data rate are about 150 – 200 Mbps and can offer up to maximum of 600 Mbps.
Cellular
Cellular technology forms the foundation of every mobile phone network. It is also utilized in Internet of Things (IoT) applications that require communication over long distances. These applications benefit from cellular communication technologies like 2G, 3G, 4G, and the upcoming 5G, which promise even faster and more reliable connectivity.
Here are some important features of cellular technology:
Capable of Transferring Large Amount of Data: Cellular technology can handle significant amounts of data, making it suitable for applications that require the exchange of large files or real-time streaming.
High Power Consumption: However, using cellular technology can consume more power compared to other IoT protocols. As a result, it may not be the best choice for devices with limited battery life or those that need to operate for extended periods without frequent recharging.
Ideal for Projects with Low Data Transfer: Cellular technology is most effective for projects that transmit small amounts of information at regular intervals, as this minimizes power consumption and allows devices to operate efficiently.
The cellular technology used in different generations has its respective standards and characteristics:
- 2G standards include GSM, EDGE, and GPRS.
- 3G standards include UMTS and HSPA.
- 4G standard is known as LTE.
Frequencies for these standards can be around 900, 1800, 1900, and 2100 MHz, depending on the region and service provider. The range of communication varies for different 2G and 3G technologies, with GSM covering about 35 km and HSPA extending to approximately 200 km.
Data rates also differ among these standards: GPRS offers speeds ranging from 35 to 170 Kbps, EDGE provides 120 to 384 Kbps, UMTS supports 384 Kbps to 2 Mbps, HSPA offers speeds of 600 Kbps to 10 Mbps, and LTE provides data rates between 3 to 10 Mbps.
In summary, cellular technology provides a robust and widely accessible means of communication for both mobile phones and IoT devices. Its capability to transfer large data sets is valuable, but it should be used judiciously in projects where power consumption needs to be carefully managed. The various standards, frequencies, and data rates cater to different use cases and connectivity requirements, making cellular technology a versatile option for a range of IoT applications.
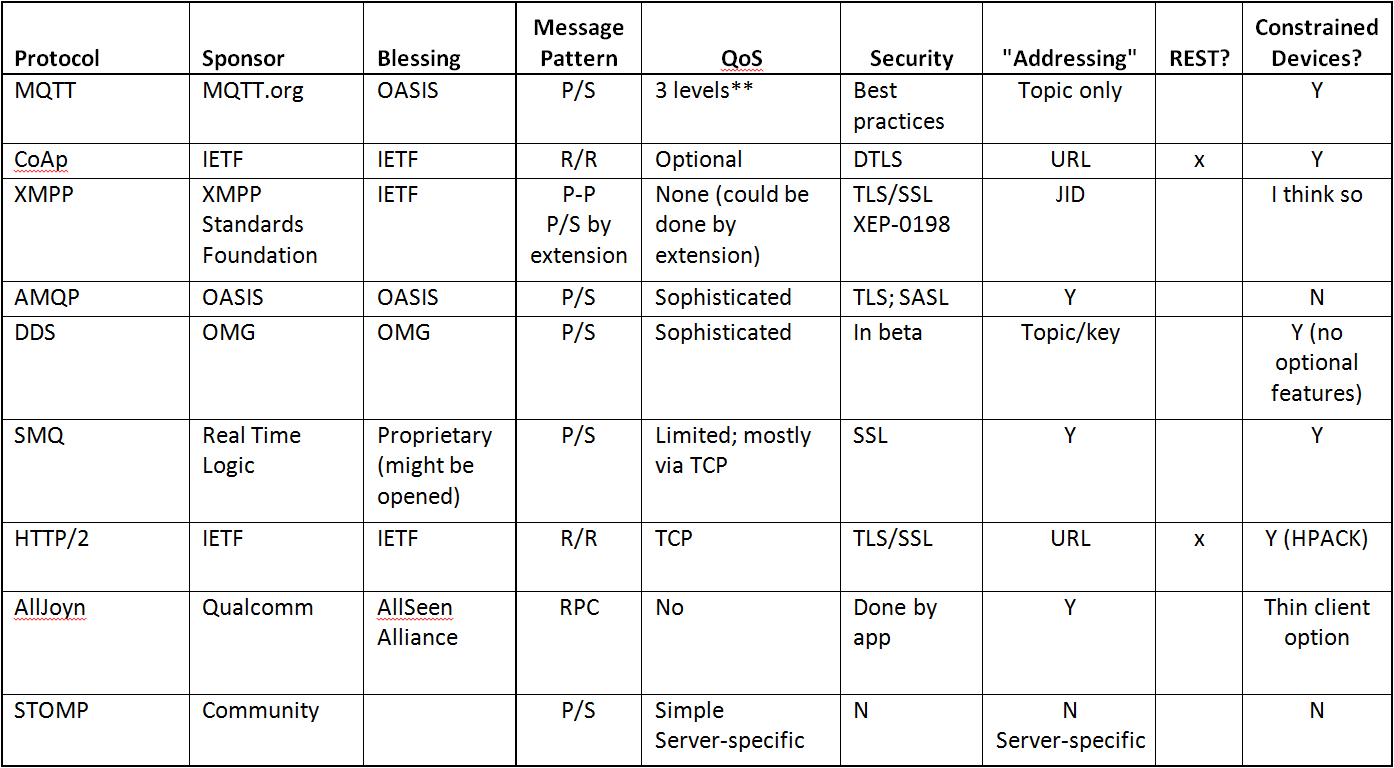
Comparison of IoT Protocols
In summary, this table provides a comparison of all protocols according to various aspects.
| IoT Protocols | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) | Zigbee | Z-Wave | Thread | Matter | LWM2M (Lightweight M2M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | 800-900 MHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz | N/A |
| Range | Up to 50 meters | Up to 10-100 meters | Up to 100 meters | Up to several kilometers | Up to 100 meters | Varies depending on the medium |
| Topology | Star or Point-to-Point | Mesh | Mesh | Mesh | Mesh | Server-client |
| Power | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Data Rate | Up to 2 Mbps | Up to 250 Kbps | Up to 100 Kbps | Up to 250 Kbps | N/A | N/A |
| Interoperability | Moderate | High | High | High | High | High |
| Security | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | High | Moderate |
| Application | IoT, Wearables, Health Monitoring | IoT, Home Automation, Lighting, Industrial | IoT, Home Automation, Security | IoT, Smart Home, Industrial | Smart Home, IoT, Home Automation | Device Management for IoT |