In this article, we will talk about photodiode. It is basically a light detector semiconductor device that converts the light energy into current or voltage. This conversion depends on the mode of operation. It has built-in optical filters and lenses and may have a large or small area of surface. When light falls on this surface, it produces a current. When there is no light falling on this surface, it also gives off a small amount of current. The current that this device produces is directly proportional to the light that falls on the surface of the photodiode. As we increase the surface area, the response time to produce current becomes shorter. We can see the schematic symbol in the figure below:

Construction of Photodiode
A photodiode is a PN junction diode that forms from two types of junctions. This has a junction of P-type semiconductor material such as boron and a junction of N-type semiconductor material such as phosphorous. For reference, we can see its construction in the figure below.

According to the figure above, it forms by the diffusion of lightly doped p-type impurities into heavily doped n-type impurities. The area between the p-type impurity and the n-type impurity is the depletion region. The contact pads are deployed in an n-type area called the cathode, and the p-type area is called the anode. In this figure, some portion of the front area is the active area. This area is coated with anti-refection material to reduce the reflection of light, and the rest of the area is called the non-active area, which is coated with a thick layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2). The responsivity and speed of the photodiode to convert the light into current are controllable via the thickness of this non-active area. The photo diode operates in reverse bias mode, which means applying negative voltage at the anode and positive voltage at the cathode.
Working Principles of Photodiode
A photodiode is made of silicon semiconductor material, which has an energy gap of 1.12 eV at room temperature. This gap is actually between the valence band and the conduction band. At zero room temperature, the valance band completely fills with the negative or positive ions. Whereas the conduction band is completely vacant, there are no negative or positive ions. As we increase the temperature, the electrons in the valence band excite more and move from the valence band to the conduction band. We call these electrons free electrons. These free electrons are free to conduct the current.
When the p-type and n-type materials form a junction, a concentration gradient forms due to this. The diffusion of holes from the p-type material region and electrons from the n-type material region develops a voltage across the junction. Hence, it forms an interdiffusion depletion region. The voltage across this depletion region produces an electric field. When we connect the photodiode in reverse bias mode, the width of this depletion region increases slowly. Eventually, this region breaks down, and the flow of current starts from the anode to the cathode. This current depends on the incident light at the surface.
Operational Modes of Photodiode
The photodiode operates in mode of operation.
- Photovoltaic Mode
- Photoconductive Mode.
- Avalanche Diode Mode
Photovoltaic Mode:
We call this mode zero-bias mode. This mode is useful in applications where we are using photodiodes at low levels of frequency as well as ultra-low levels of light. This mode provides very low-level current variation and nonlinear behavior in voltage production.
Photoconductive Mode
In this mode, the photodiode is in reverse bias mode. When we use a photodiode in this mode, the length of the depletion region increases. But the capacitance of the junction and the response time decrease. In this mode, the current increases linearly as the incident light increases. It is very fast, but it displays electronic noise.
Avalanche Diode Mode
We use this mode in high-reverse bias conditions. The photodiode works in the avalanche breakdown region. In this mode, the internal gain and responsiveness of the device increase.
V-I Characteristics of Photodiode
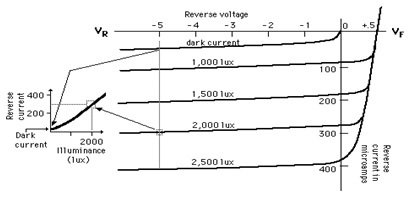
It always operates in reverse bias mode. We can see the V-I characteristic in the figure below. This figure plots reverse voltages horizontally in volts and reverse currents vertically in microamperes. According to the figure, the reverse current is almost independent of the reverse voltage. When the illumination is zero, the reverse current is approximately zero. But only a small amount of current is present, and this current is the dark current. The reverse current increases linearly as the illumination increases. We can see that at illumination of 1000 lux, the reverse current is 100 microamperes; at illumination of 1500 lux, the reverse current is 200 microamperes. Whereas at illumination of 2000 lux, the reverse current is 300 microamperes, etc. This means that the reverse current increases linearly. We can see this linearly increasing current in the figure.
Types of Photodiodes
Mainly, the photodiode is divided into four types.
- PN junction
- Avalanche
- PIN Photodiode
- Schottky Photodiode
PN Junction Photodiode
It is the first and most simple form that we use at the beginning. After this, so many technologies were developed. But currently, this type of diode is not commonly in use. Its uses are low-frequency and for sensitive applications.
Avalanche Photodiode
This type of photodiode is useful in areas where the light has low intensity. The avalanche photodiode provides a high level of gain but also produces a high level of noise; therefore, this type is not applicable for all applications.
PIN Photodiode
This is actually a p-i-n junction photodiode. Although this is not the first form, this type is currently in so many applications. This PIN junction collects the photons of light more efficiently than the PN junction photodiode. This type of photodiode also offers a lower capacitance than the other types.
Schottky Photodiode
We can see from the name of this type of photodiode that it belongs to the Schottky diode, which is for high-frequency switching. This type of diode has high-speed capability. It offers lower capacitance and a high bandwidth of communication.
Applications of Photodiode
- These are useful in photoconductors, photomultiplier tubes, and charged-coupled devices to generate the output signal, which depends upon the light illumination.
- We use them in electronics devices such as smoke detectors, compact disk players, and infrared remote controls. Which are used on the television, LCD, and other devices.
- They have uses in science and industry for accurate measurement of light intensity and show more linear behavior than photoconductors.
- They are widely used in medical equipment such as computerized tomography (CT scan).
- PIN photodiodes are more sensitive and faster than PN photodiodes; therefore, these are used for light regulation and optical communication.
- These are also used in cameras, safety equipment, position sensors, bar code sensors, automotive devices, and surveying instruments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this tutorial provides an in-depth overview of photodiodes, their construction and workings. It also covers their operational modes, types and application to help us better understand the concept. You can utilize this knowledge in your project to make it more efficient and effective. Hopefully, this article was helpful in expanding your knowledge,
You may also like to read:
- Multilevel Inverters with Introduction, Types, Advantages and Applications
- types of oscillator used in microcontrollers
- ESP8266 NodeMCU HTTP POST using Arduino IDE (ThingSpeak and IFTTT)
- UC2842 Current PWM Controller IC
- INA219 Current Sensor Module with Arduino – Print values on OLED
- BeagleBone Black Pinout, Pin Configuration and Features
This concludes today’s article. If you face any issues or difficulties, let us know in the comment section below.

