In this tutorial, we will look at wireless sensor networks. Wireless sensor networks are a group of specialized devices or sensors that we can use to monitor different environmental conditions and collect and organize that data at a certain central location. It detects and measures a number of physical conditions, such as humidity, temperature, sound, pressure, speed and direction, chemical concentrations, vibrations, pollutant levels, and many other such conditions. It has many applications in microcontroller projects.
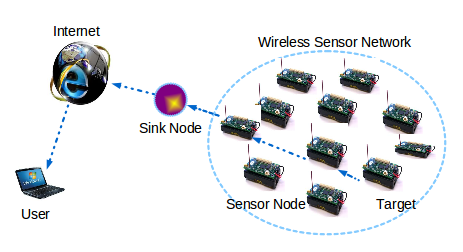
There are a number of nodes in a sensor network; these nodes are the detection stations, and they are very small and portable. There is a sensor/transducer, microcontroller, transceiver, and power source in every sensor node. The transducer senses the physical condition, and if there is any change, it generates electrical signals. These signals go to the microcomputer for processing. A central computer sends commands to the transceiver and transmits the data to that computer.
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) Topologies
There are four common sensor network topologies:
- Point to point network
- Star network
- Tree network
- Mesh network
We will discuss each of them briefly.
1. Point to Point Network Topology
In this topology, there is no central hub. A node can communicate directly with another node. This is the most common topology, and it has a single data communication channel that offers a secure communication path. Each device can act as a client and a server in it.
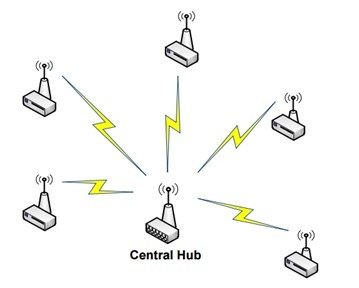
2. Star Network Topology
Unlike point-to-point networks, a centralized communication hub is present in a star network. Each communication is done through this centralized hub, and no direct communications between the nodes are possible. In this case, the central hub is the server, and the nodes are clients.
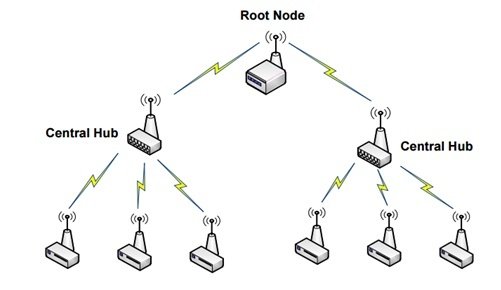
3. Tree Network Topology
This topology is said to be a hybrid of point-to-point and star topologies. The central hub in it is called a root node or the parent node. Data is passed on from leaf nodes to the parent node. The main advantage of this topology is less power consumption as compared to other networks.
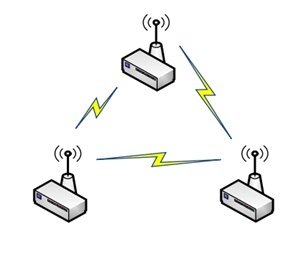
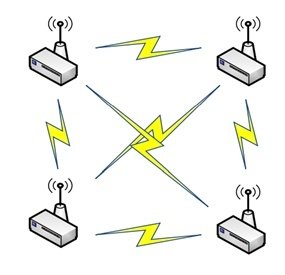
4. Mesh Network Topology
In the mesh network, the data can ‘hop’ from one node to another. All the nodes can communicate with each other directly without having to depend on a central communication hub. This is the most reliable structure of network communication because there is no single point of failure in it. But this structure is very complex and requires a lot of power consumption.
Types of Wireless Sensor Networks
There are different types of sensor networks, such as underground, underwater, terrestrial, multimedia WSNs, etc. We will discuss them briefly.
1. Terrestrial WSNs
These types of networks consist of hundreds or thousands of wireless sensor nodes. These nodes can be deployed in an unstructured or structured manner. The nodes are distributed randomly in an unstructured mode, but they are kept within the target area.
These are the ‘terrestrial’ sensor networks; therefore, they are above ground, and solar cells can be used to power up these networks. Energy can be conserved by minimizing delays and by using low-duty cycles, etc.
2. Underground WSNs
These sensor networks are more costly as compared to terrestrial networks. The equipment used is expensive, and proper maintenance is needed. These are effectively used to monitor the underground conditions; therefore, their whole network is underground, but to pass on the information to the base station, sink nodes are used, which are present above the ground.
We face problems while recharging the batteries of the underground sensor networks, and loss of signal can also occur due to the high level of attenuation in the underground environment.
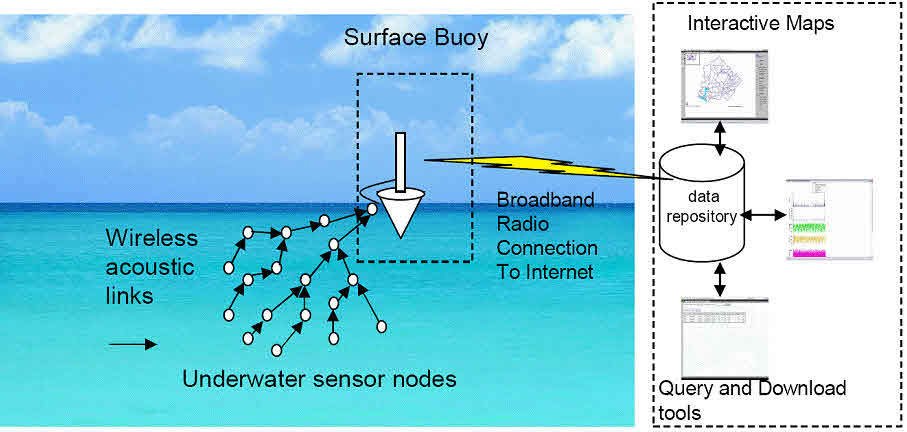
3. Underwater WSNs
Underwater wireless sensor network systems consist of sensor nodes and vehicles that deploy under the water. The use of underwater vehicles is to gather data from the sensor nodes. The long propagation delay and sensor failures are a big challenge to the underwater communication system. The battery of these WSNs has a limit and is not rechargable; therefore, the pursuit of developing different techniques to solve this issue of energy usage and conservation is in progress.
4. Multimedia WSNs
These sensor networks can gather information in the form of audio, video, and imaging. The sensor nodes in these networks connect with cameras and microphones. They can track and monitor different events occurring and keep a visual display of the events as well. For the purposes of data compression, retrieval, and correlation, these nodes also interconnect with one another through a wireless connection.
Since audio and visual data transmit through these networks, they require high power consumption and bandwidth. Hence, they use advanced techniques of data processing and compression.
5. Mobile WSNs
The mobile network, as the name suggests, is not fixed; rather, the sensor nodes can move from one place to another. They can easily interface with the environment around them. Their main advantage is that they provide better coverage, superior channel capacity, and enhancements in coverage. These mobile WSNs are more versatile in comparison to the other static sensor network systems.
Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks
There are numerous applications of WSNs in industrial automation, traffic monitoring and control, medical device monitoring, and many other areas. We will discuss some of the applications below:
1. Disaster Relief Operation
If a report of an area facing some sort of catastrophe arises, such as a wildfire, then drop the sensor nodes on the fire from an aircraft. Monitor the data at each node and construct a temperature map to devise proper ways and techniques to overcome the fire.
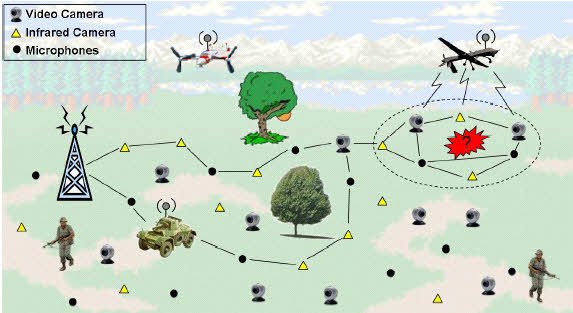
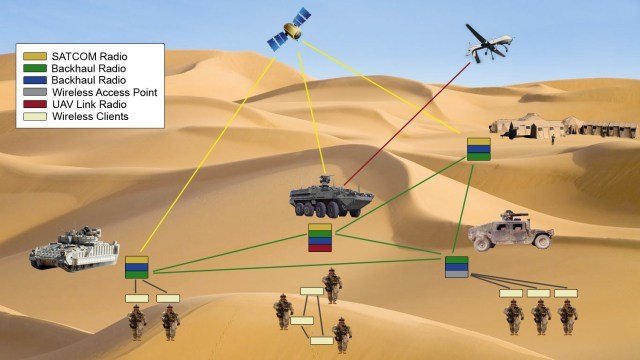
2. Military Applications
The WSNs can deploy rapidly and have self-organizing properties; therefore, they are very useful in military operations for sensing and monitoring friendly or hostile motions. We can easily do battlefield surveillance through the sensor nodes to keep a check on everything in case there are more equipment, forces, or ammunition requirements on the battlefield. Chemical, nuclear, and biological attacks are also detectable through the sensor nodes.
An example of this is the “sniper detection system”, which can detect incoming fire through acoustic sensors and estimate the position of the shooter by processing and detecting audio from the microphone.
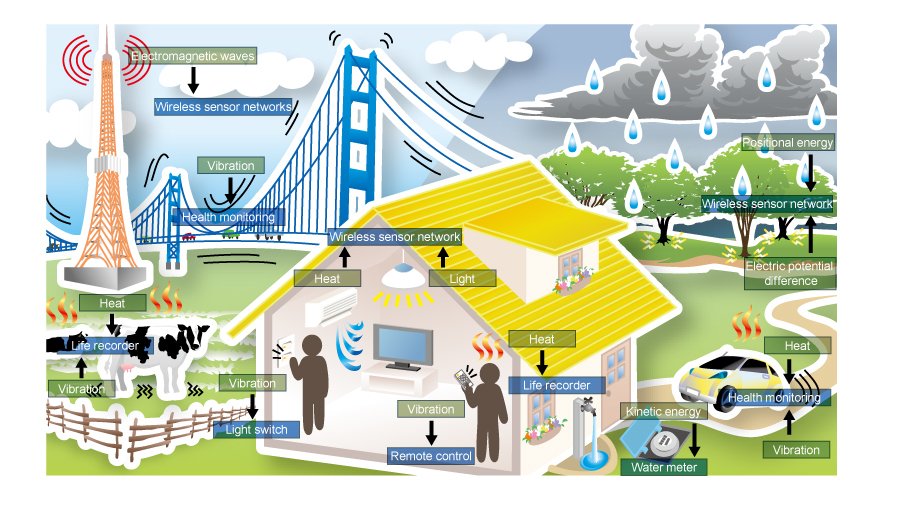
3. Environmental Applications
These sensor networks have a huge number of applications in the environment. They are useful to track the movements of animals and birds and record them. Monitoring of the earth, soil, atmospheric context, irrigation, and precision agriculture is doable through these sensors. They also have uses for the detection of fire, floods, earthquakes, chemical or biological outbreaks, etc.
A common example is the “Zebra Net”. The purpose of this system is to track and monitor the movements and interactions of zebras within themselves and with other species as well.
4. Medical Applications
In health applications, the integrated monitoring of a patient can be done by using WSNs. We can also monitor the internal processes and movements of animals, along with diagnostics. They also help in keeping a check on drug administration in hospitals and in monitoring patients as well as doctors.
An example of this is the “artificial retina”, which helps the patient detect the presence of light and the movement of objects. They can also locate objects and count individual items.
5. Home Applications
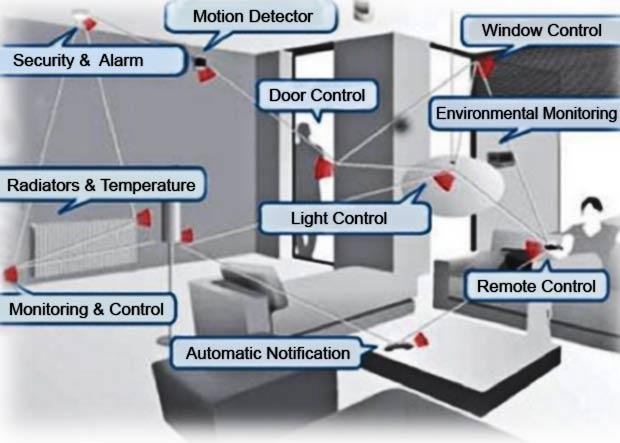
As technology advances, it is also making its way into our household appliances for their smooth running and satisfactory performance. These sensors can be found in refrigerators, microwave ovens, vacuum cleaners, security systems, and also in water monitoring systems. The user can control devices locally as well as remotely with the help of the WSNs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this tutorial provides an in-depth overview of wireless sensor networks. It covers their basic introduction with different types of topologies and sensors along with practical applications. You can utilize this concept for you project. Hopefully this was helpful in expanding your knowledge.
You may also like to read:
- Raspberry Pi Pico W Wireless BME280 Web Server
- Interface nRF24L01+ Wireless Module with Arduino
- NRF24L01 Wireless RF Module Complete Guide
- Wireless Temperature Sensor using GSM and Microcontroller
- Reconnect ESP32 to WiFi after Lost Connection (Solved)
- Control ESP32 Outputs using Google Assistant and Adafruit IO
This concludes today’s article. If you face any issues or difficulties, let us know in the comment section below.




what types of micro controller would be used for wireless sensor especially in Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) ?
any microcontroller can be used
sorry wrong question
how can we implement wireless sensor network in matlab? please provide its code and research matter..
if you find this…matterial plz send me Abidkhan3141@gmail.com