In this tutorial, we will discuss the workings of conventional capacitors and their types. This is a passive device that stores electric energy in the form of a static electric field. It consists of two plates that are electrodes, and an insulating layer separates these electrodes. When it connects with a battery or any energy source, positive charges add up at the positive electrode. Similarly, the negative charges add up at the negative electrode, but both charges cannot mix up due to the insulating layer.
If we remove an energy source, then an electric field will always be present at the electrode plates. Now, we short both electrodes through a conductor. When this shorts through a conductor, then current flows in this specific conductor at that time until the potential difference between both plates is the same. This is the basic working phenomenon of a capacitor. The working phenomena of every capacitor are the same, but they are available on the market in different types and sizes. You may also like to check out the types of inductors.
Introduction to Capacitors
These types and sizes are based on their voltage level and value of capacitance. The first capacitor was invented by Pieter van Musschenbroek in 1746, who was a professor in Holland at the University of Leyden (or Leiden). At that time, the name of the invented capacitor was Leyden Jar, which was made with the help of a glass jar.
To make this out of the glass jar, he wrapped thin metal foil inside and outside of the jar. Then connect the outer side of this jar to the ground and the inner side to an energy source such as a generator. Even at that time, he did not know how it would work. He did so many experiments on this, but he could not get any results. At the end, mistakenly, when he picked up the jar, he suddenly felt a heavy electric shock, and he understood he had discovered a capacitor. At that time, this glass jar had been used as a capacitor, but later on, after so much research, a proper shape was discovered. Now the capacitor has become the most commonly used component in electronic circuits.
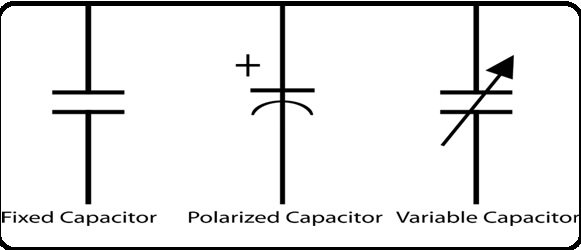
It plays an important role in electronic design circuits and embedded system applications. Different symbols, such as fixed, variable, and polarized capacitor symbols, are shown in the figure below.
Types of Capacitors
This is a very significant component in electronic devices. Their manufacturing occurs in millions of quantities on a daily basis. There are so many types on the market. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, but a little knowledge about these capacitors is necessary for the user so that they can choose the correct one for any special-purpose application.
Electrolytic Capacitors
It is the type of capacitor that is mostly polarized, and it is widely used in those palaces where high capacitance is required. Normally, in some places, we use thin-film metallic capacitors, which consist of only a single electrode. But at other places, semi-liquid electrolytic capacitors are a very suitable solution and are available in the form of jelly or paste, which works as a second electrode.
Because it consists of a thin layer of oxide material that is grown electrochemically in less than ten microns with the thickness of a film, when it is used in a circuit or anywhere, one must care about its polarity. The negative terminal connects with the negative power supply terminal, whereas the positive terminal connects with the positive power supply terminal; otherwise, its opposite polarity will damage the insulation oxide layer, which will damage the capacitor permanently. These work with a DC power supply and are available above 1 microfarad. For a simple electrolytic capacitor, refer to the figure below.

Ceramic Capacitors
A ceramic capacitor is one that is made of ceramic or porcelain material. The physical shape of these is like a disc; therefore, they are also known as disc-type capacitors. Because it has a very low capacitance value, the physical size of these capacitors is mostly 3 to 6 mm. It has a high dielectric strength constant (HIGH-K), so a high value of capacitance could be merged into a small size. Its capacitance does change with temperature; therefore, they are used as decoupling or by-pass capacitors, and these are non-polarized capacitors. These are available on the market in the range between pico farads and one or two micro farads. They are mostly used in audio and RF applications. They are less costly and more reliable, and their loss factor is relatively low as compared to other types. A simple ceramic capacitor is shown in the figure below.

Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors
Tantalum electrolytic capacitors are also polarized just like electrolytic capacitors, and they offer a very high level of capacitance value. Its behavior is very intolerant during reverse biased conditions, and it cannot bear high voltage or ripple current above a certain level. They are easily available on the market in both leader and surface mount formats. However, some of these types contain two capacitors in a single body, and in these types, the negative terminal is connected to a negative power supply to form a non-polarized capacitor, which is mostly used in low voltage AC circuits. Similarly, the positive terminal is marked at its body, and the overall shape of this is just like geometry. Its typical values are available in the range of 47 nF to 470 uF. A simple tantalum electrolytic capacitor is shown in the figure below.

Variable Capacitor
It is the type of capacitor whose capacitance values could be changed by the user intentionally by moving the knob mechanically. These types are mostly used to set the resonance frequency in LC filter circuits, and they are also used as signal processing devices, energy storage systems, and motor starter systems. A simple variable capacitor is shown in the figure below.

Silver Mica Capacitor
It is the type of capacitor that is not mainly used, but it still offers a high level of stability, low loss, and high accuracy where space is not an issue. They are mostly used in RF applications, but they are available in limited values such as 1000 pF and so on. Their cost is so high as compared to other types. Some simple silver mica capacitors are shown in the figure below.
Polystyrene Film Capacitor
It is the type of capacitor that is very cheap in comparison to the other types, but it offers close tolerance where the need arises. They offer a tolerance of about 5% to 10%, which is suitable for many applications. They are available in the form of Leader electronic components. We can see some simple polystyrene film capacitors in the figure below.

Glass Capacitor
In glass capacitors, the dielectric material is glass. They offer a high level of working performance, low loss, and high current carry capability, but they are so costly in comparison to other types. For a simple glass capacitor, refer to the figure below.

Conclusion
In conclusion, this tutorial provides an in-depth overview of capacitors and their types. In this tutorial, we discuss seven types of capacitors to better grasp and understand their concepts. Hopefully, this was helpful in expanding your knowledge.
You may also like to read:
- Introduction to Inductor and its Types
- FSR 400 Force Sensing Resistor introduction
- ESP32 ESP-NOW Getting Started Tutorial with Arduino IDE
- ESP8266 NodeMCU SHT31 Temperature and Humidity Web Server
- ESP32 ESP-NOW Two way Communication (Arduino IDE)
- Introduction to Double layer PCB – Construction and working
- UART Communication with Pic Microcontroller (Programming in MPLAB XC8)
- Calculate Factorial of a Number in LabView: Tutorial 35
- FOD3180 MOSFET Gate Driver Optocoupler
- BME680 with ESP32 using Arduino IDE (Gas, Pressure, Temperature, Humidity)
This concludes today’s article. If you face any issues or difficulties, let us know in the comments section below.


I am interested to find out the values of ceramic capacitor to give enough oscillator drive pulse
Current for PIC 16f 18f & arduino operations