In this home automation project using Arduino, we will use voice function to control home devices. This project is similar to home automation using Bluetooth. In that project, we used the S2 Terminal application however in this project we will use AMR_Voice Android application. This application is free and very easy to use. People of any age can control it by just speaking the commands. So let us begin!
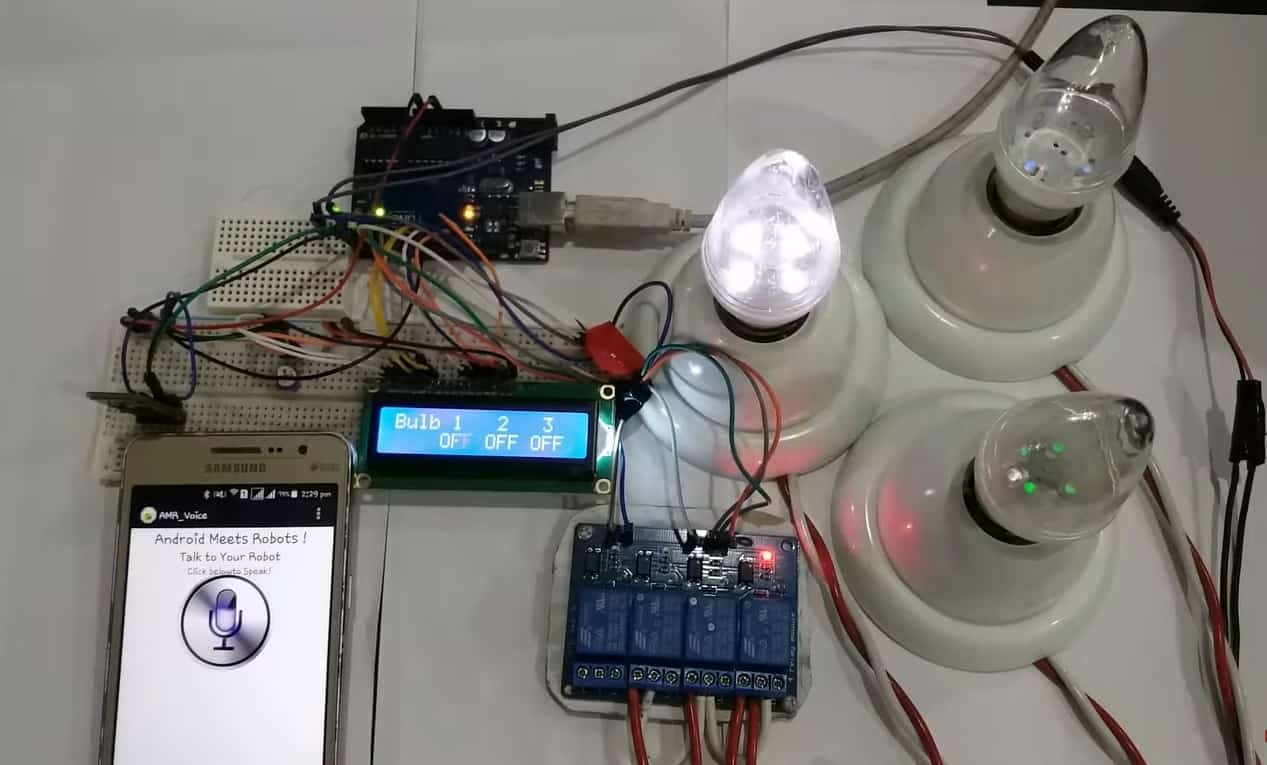

Voice Controlled Home Automation System Overview
We will require the following components for this project.
Required Components:
- Arduino Uno: We will use Arduino due to its simplicity and it also provides several digital pins to interface with LCD and relay module at the same time. It is very useful when you prototyping a project.
- HC-05 Bluetooth Module: HC-05 is one of the commonly used Bluetooth device that uses UART communication protocol.
- 4 Channel Relay Modules: Relay is used to switch on and off higher voltage devices by using low dc voltages such as signal from the Arduino digital pin. In this project, we will use 4 channel relay module. It is easy to interface with Arduino instead of connecting each relay separately. It can bear up to 250VAC and 10 amps of current.
- 16×2 LCD: 16×2 LCD is used to display 16 characters in two lines. It is easy to interface with Arduino due to its available library. We will use 16×2 LCD because it is easy to interface with Arduino and very cheap in price. A 10k potentiometer is used to control the contrast of display. In this project, this LCD is used to display the status of the appliances.
- AC bulbs with holders: AC bulbs are used to represent devices and appliances. Because it is easy to handle and very useful when you are prototyping any AC project. In the final product, you can just replace it with an AC socket to control.
- AC wire with plug: Use good quality wire when working with higher voltages. It is always good to use electrical tape to cover connections.
- External 5 volt supply: 5 volt dc supply is required to switch the relay ON and OFF. Otherwise, it does not work. Also do not supply 5v from Arduino.
How does Voice Control Home Automation Work?
In this voice-controlled home automation system, Arduino Uno is used as the brain of our circuit.
You can view the operations constituting the voice control home automation system in the block diagram below
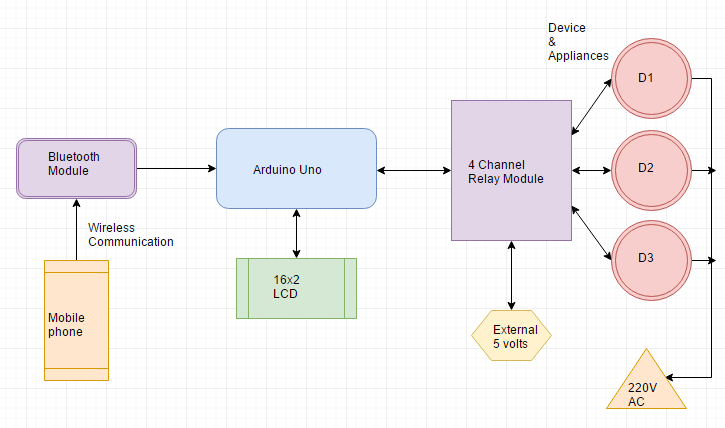
Connection Diagram of Voice Controlled Home Automation Project
In this section, we will explain the connections of the various components specified above with Arduino Uno to form the home automation system.
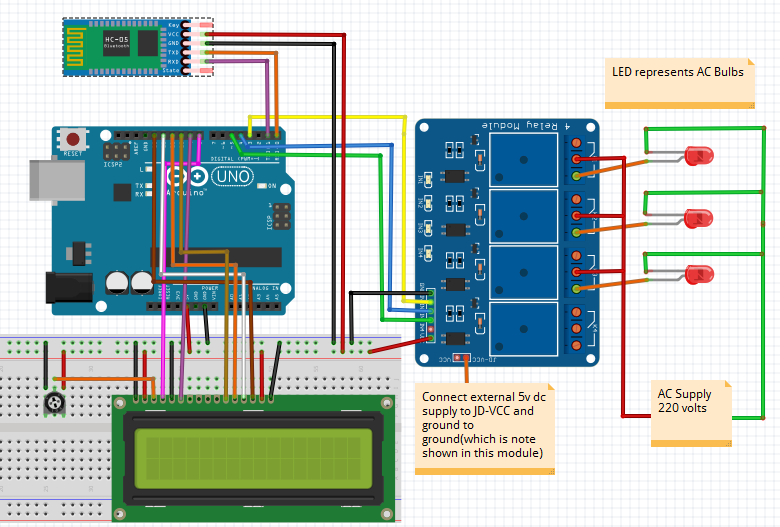
Let us discuss them one by one.
Arduino with HC-05 Bluetooth Module
The HC-05 comes with multiple pins and indicators, which helps to control different operations and view their states through indicators. This pinout diagram provides indications of all pins.
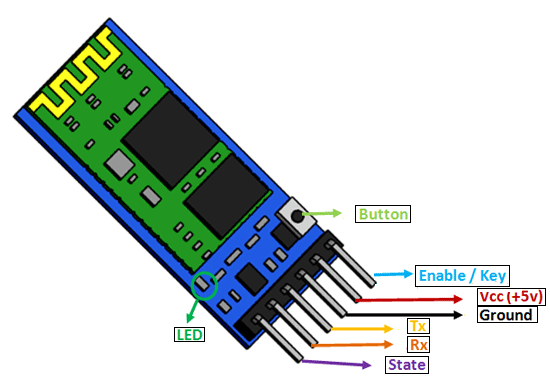
However, we will use 4 of these pins to connect with Arduino. These include the VCC, GND, RX, and TX pins.
The connection of the HC-05 Bluetooth module with Arduino UNO is very easy as we will be using the serial communication interface that consists of two pins TX and RX. As you know, in order to communicate with the HC-05 Bluetooth module, we need to use a UART communication port of the Arduino board.
RX and TX pins of the module will be connected with the UART pins of Arduino UNO. Arduino Uno has a single UART interface found on pin 0 (RX0) and pin 1 (TX0).
The table below shows the connections that we will use to connect the two devices:
| HC-05 | Arduino UNO |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX | pin 0 (RX) |
| RX | pin1 (TX) |
Recommended Reading: HC-05 Bluetooth Module Interfacing with Arduino with LED Control Example
Arduino with 16×2 LCD
We will use a 16×2 LCD in our project to display the states of the appliances. To connect a 16×2 LCD with Arduino we will require an additional 10k potentiometer as well.
We have a dedicated tutorial regarding interfacing 16×2 LCD display with Arduino with some example sketches. Have a look at it before proceeding further for a better understanding of the LCD.
Recommended Reading: 16×2 LCD Interfacing with Arduino – Explained with Example Codes
There are two types of pins on the whole 16×2 LCD module. Some pins are used to send to 16×2 LCD and some are command pins. In other words, every pin has a role in controlling a single pixel on the display.16 x 2 LCD has sixteen columns and two rows. That means, it can display sixteen characters per row and it has two such rows.
Pinout
The diagram shows the pin configuration of a 16×2 LCD display. It has sixteen pins.
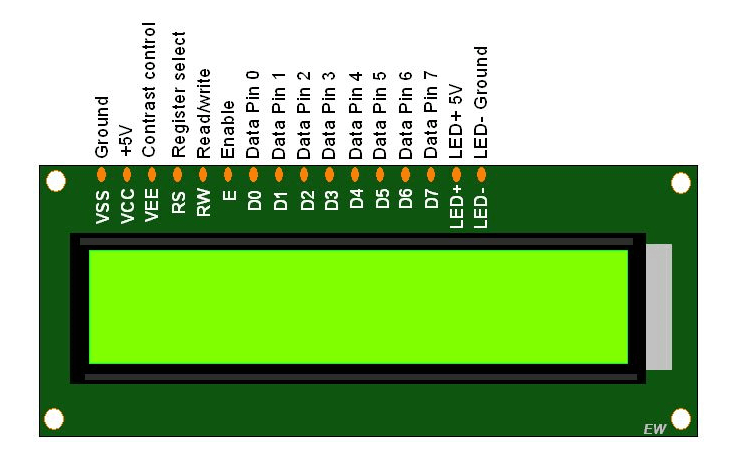
- D0 – D7: Pin number 7-14 are data bus lines that are used to send data from Arduino which you want to display on LCD. With these 8 data lines, data can be transferred either in an 8-bit format or in a 4-bit format. In a 4-bit format, only upper four bits (D4-D7) are used to send data from Arduino to LCD. The full byte is transmitted in two successive transmissions. A 4-bit format is used to save GPIO pins of Arduino. Because fewer GPIO pins of Arduino will be required to transfer data.
- Contrast Select (VEE): It will help to control the contrast of PIXELS according to the 16X2 LCD light.
- RS: This pin is known as a register select pin. It helps to toggle the command/data register.
- R/W: The signal on this pin will decide whether it is going to read from LCD or write on it.
- EN: Enable pin will help to transfer the instruction from the data pins and another command pin to the LCD. It act as permission to internal registers.
- VSS: It’s a ground pin for common grounds.
- VCC: The power pin will use for voltage input to the 16X2 LCD.
Arduino connections with 16×2 LCD
We are using the following connections as described below. Refer to the schematic diagram to have a clearer idea of the connections.
| 16×2 LCD | Arduino |
|---|---|
| D4 – D7 | Pin 10,11,12,13 |
| Enable | Pin 9 |
| RS | Pin 8 |
| RW | GND |
| VEE | 10k POT (Middle Leg) |
| VSS | GND |
| VCC | +5V |
| LED+ | +5V |
| LED- | GND |
We have an Arduino library for easy communication between LCDs called the LiquidCrystal library. It is an inbuilt library by Arduino Adafruit version.
You can read more here:
Arduino with Channel Relay modules
The relay module for Arduino is one of the most powerful applications for Arduino as it can be used to control both A.C and D.C devices by simply controlling the relay by giving 5V. A relay is basically a switch which is operated electrically by an electromagnet. A relay can be used to control high voltage electronic devices such as motors as well as low voltage electronic devices such as a light bulb or a fan.
We will be using the 4 relay Arduino module in our home automation project.
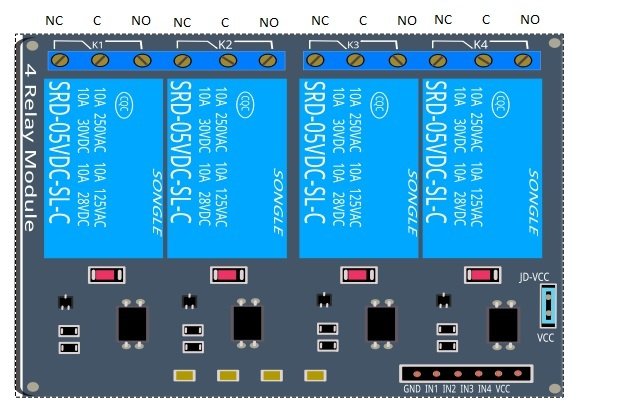
- External 5 volt to JD VCC.
- Ground to ground.
- IN1 to Pin 3.
- IN2 to Pin 4.
- IN3 to Pin5.
- VCC to Arduino 5v.
- Connect one end of all bulbs to the normally open terminal of relays.
- One end of 220VAC to all common terminals of relay and other ends with other terminals of the light lamps.
Working Voice Controlled Home Automation using Arduino
Throughout this guide, we will use an android smartphone that will connect to our Arduino development board. So, make sure you have an android phone at hand.
Go to the Play Store and download the application by the name: AMR_Voice.
Open the application and speak the specified commands. The application sends the command to Bluetooth which is then received by Arduino which performs the described task. At the same time, the Arduino displays the status of the appliances on the LCD.
For demonstration purposes, we will use different colored bulbs: white, blue, and green.
Each command has its unique operations which are defined in code. You can change the commands according to your ease. Below is the list of commands that the user will speak to control the bulbs.
| Voice Commands sent from mobile | Function |
|---|---|
| white on | White Bulb turns ON |
| white off | White Bulb turns OFF |
| blue on | Blue Bulb turns ON |
| blue off | Blue Bulb turns OFF |
| green on | Green Bulb turns ON |
| green off | Green Bulb turns OFF |
Voice Controlled Home Automation System Arduino Code
We will use Arduino IDE to program our Arduino board. Open your Arduino IDE and go to File > New to open a new file. Copy the code given below in that file and save it.
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13);
#define white 3
#define blue 4
#define green 5
int tx = 1;
int rx = 0;
char inSerial[15];
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(white, OUTPUT);
pinMode(blue, OUTPUT);
pinMode(green, OUTPUT);
pinMode(tx, OUTPUT);
pinMode(rx, INPUT);
digitalWrite(white, HIGH);
digitalWrite(blue, HIGH);
digitalWrite(green, HIGH);
lcd.begin(16, 2);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("MICROCONTROLLERS ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" LAB ");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("VOICE CONTROL");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("HOME AUTOMATION ");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("1. Bulb 1 WHITE");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("2. Bulb 2 BLUE");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("3. Bulb 3 GREEN");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Bulb 1 2 3 ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" OFF OFF OFF");
}
void loop() {
int i = 0;
int m = 0;
delay(500);
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
inSerial[i] = Serial.read();
i++;
}
inSerial[i] = '\0';
Check_Protocol(inSerial);
}
}
void Check_Protocol(char inStr[]) {
int i = 0;
int m = 0;
Serial.println(inStr);
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*white on#")) {
digitalWrite(white, LOW);
Serial.println("White ON");
lcd.setCursor(4, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*white off#")) {
digitalWrite(white, HIGH);
Serial.println("White OFF");
lcd.setCursor(4, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*blue on#")) {
digitalWrite(blue, LOW);
Serial.println("Blue ON");
lcd.setCursor(8, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*blue of#")) {
digitalWrite(blue, HIGH);
Serial.println("Blue OFF");
lcd.setCursor(8, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*green on#")) {
digitalWrite(green, LOW);
Serial.println("Green ON");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*green of#")) {
digitalWrite(green, HIGH);
Serial.println("Green OFF");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
else {
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
}How does the Code Work?
We will start by including the library required for our 16×2 LCD as shown below:
#include<LiquidCrystal.h>Next, we declare the Arduino pins that are connected with the LCD. To define connections, we use the following line of code. This line creates a LiquidCrystal object and lcd is a name of the object that we are going to use to call LCD functions. You can also use any other name.
LiquidCrystal lcd(rs, en, d4, d5, d6, d7)In our case, the pins are 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13 respectively.
LiquidCrystal lcd(8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13);Specify the Arduino pins connected with IN1, IN2 and IN3 of 4 Channel Relay Module. These pins will control white, blue and green bulbs.
#define white 3
#define blue 4
#define green 5Moreover, also specify the Arduino digital pins connected with TX and RX pins of the HC-05 module.
int tx = 1;
int rx = 0;Also, we create an array of 15 characters called inSerial that we will use later on in the code to monitor the states of the bulbs.
char inSerial[15];setup()
Open the serial communication at a baud rate of 9600.
Serial.begin(9600);Configure the pins connected with the bulbs and the TX pin as output pins and the RX pin as an input pin. This is done by using the pinMode() function. Specify the pin as the first parameter and the mode as the second parameter.
pinMode(white, OUTPUT);
pinMode(blue, OUTPUT);
pinMode(green, OUTPUT);
pinMode(tx, OUTPUT);
pinMode(rx, INPUT);
Moreover, set the value of the pins connected with the three bulbs to HIGH by using digitalWrite() function. Specify the pin as the first parameter and the value as the second parameter. This will ensure that all the bulbs are off initially.
digitalWrite(white, HIGH);
digitalWrite(blue, HIGH);
digitalWrite(green, HIGH);Next, we use lcd.begin() routine to define the size of an LCD. The first argument to this function is a number of rows and the second argument is a number of columns. For instance, this line declares the size as 16 columns and 2 rows. That means 16×2 size.
lcd.begin(16, 2);Print a series of messages on the LCD display with delays in between. Initially all the three bulbs are off hence it will be displayed on the LCD.
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("MICROCONTROLLERS ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" LAB ");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("VOICE CONTROL");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("HOME AUTOMATION ");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("1. Bulb 1 WHITE");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("2. Bulb 2 BLUE");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("3. Bulb 3 GREEN");
delay(2000);
lcd.clear();
lcd.print("Bulb 1 2 3 ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" OFF OFF OFF");
loop()
Inside the infinite loop() we first check if serial data is available in the buffer. If data is found then the characters are added one by one to the array ‘inSerial’ using a while loop. Then we will call the Check_Protocol() function with ‘inSerial’ as an argument inside it. This function will be responsible for controlling the bulbs by comparing the received data with a predefined string.
void loop() {
int i = 0;
int m = 0;
delay(500);
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
inSerial[i] = Serial.read();
i++;
}
inSerial[i] = '\0';
Check_Protocol(inSerial);
}
}Check_Protocol(char inStr[])
The Check_Protocol() function takes in an array of characters as an argument inside it.
This function is responsible for controlling the bulbs by comparing the strings received in the buffer with a predefined string. In the first case, if the command ‘white on’ was sent, then the white bulb will turn ON. If the command ‘white off’ was sent, then the white bulb will turn OFF. Likewise, if the command ‘blue on’ was sent, then the blue bulb will turn ON. If the command ‘blue off’ was sent, then the blue bulb will turn OFF. Likewise, the green bulb will be controlled similarly with commands ‘green on’ and ‘green off’.
The LCD will display all the states of the three bulbs as they change at each command.
void Check_Protocol(char inStr[]) {
int i = 0;
int m = 0;
Serial.println(inStr);
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*white on#")) {
digitalWrite(white, LOW);
Serial.println("White ON");
lcd.setCursor(4, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*white off#")) {
digitalWrite(white, HIGH);
Serial.println("White OFF");
lcd.setCursor(4, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*blue on#")) {
digitalWrite(blue, LOW);
Serial.println("Blue ON");
lcd.setCursor(8, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*blue of#")) {
digitalWrite(blue, HIGH);
Serial.println("Blue OFF");
lcd.setCursor(8, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*green on#")) {
digitalWrite(green, LOW);
Serial.println("Green ON");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print("ON ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
if (!strcmp(inStr, "*green of#")) {
digitalWrite(green, HIGH);
Serial.println("Green OFF");
lcd.setCursor(12, 1);
lcd.print("OFF ");
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
else {
for (m = 0; m < 11; m++) {
inStr[m] = 0;
}
i = 0;
}
}Demonstration
Make sure you choose the correct board and COM port before uploading your code to the board. Go to Tools > Board and select Arduino UNO. Next, go to Tools > Port and select the appropriate port through which your board is connected.
Click on the upload button to upload the code to the board. Installed this Andriod app on your smartphone.
After you have uploaded your code to the development board and have installed the application on your smartphone, open the application and connect it with the HC-05 Bluetooth module. After pairing is completed. You can speak an appropriate command as defined in the code. As a result, the bulbs will light up in response. The LCD will also display the current state of the three bulbs.
Watch the video demonstration below:
You may also like to read:


Sir plzz email the project code plzz sir..
sir please send me project code voice app please sir urgent.
Sir can you tell me the proper code i could not understand where it start and where it ends
sir can you mail me proper codes for project
is there code error?
please share the error you are facing?
Sir plz help LCD dont give display and off commands are not working